For adults with T2D who have high risk or established ASCVD
The 2021 ADA Standards of Care recommend a GLP-1 RA or an SGLT-2i with proven CVD benefit, regardless of baseline or HbA1c target, or metformin use.1
_______________________________________________________________
For adults with T2D and ASCVD or high/very high CV risk
The 2019 ESC Guidelines recommend addition of GLP-1 RA or SGLT-2i with proven CV benefit initially or directly following metformin to reduce CV events.2
_______________________________________________________________
For adults with T2D and ASCVD or high/very high CV risk
The ACC and AHA guidelines recommend considering a GLP-1 RA or SGLT-2i as conjunctive therapy for primary prevention of CVD.3,4
_______________________________________________________________
For adults with T2D who have high risk or established ASCVD, CKD or
HF
The use of a GLP-1 RA or SGLT-2i with proven CVD benefit should be considered independently of baseline HbA1c or individualised HbA1c target.5
American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(suppl 1):5111-5124.
Cosentino F, Grant PJ, Aboyans V, et al. 2019 ESC guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD: the task force for diabetes. pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Eur Heart J. 2020;41(2):255-323. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehz486
Das SR, Everett BM, Birtcher KK, et al. 2020 expert consensus decision pathway on novel therapies for cardiovascular risk reduction in patients with type 2 diabetes: a report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76:1-29. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2020.05.037
Rangaswami J, Bhalla V, de Boer IH, et al. Cardiorenal protection with the newer antidiabetic agents in patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;142(17):e265-e286. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000920
Garber AJ, Handelsman Y, Grunberger G, et al. Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm-2020 executive summary. Endocr Pract. 2020;26(1):107-139. doi:10.4158/CS-2019-0472
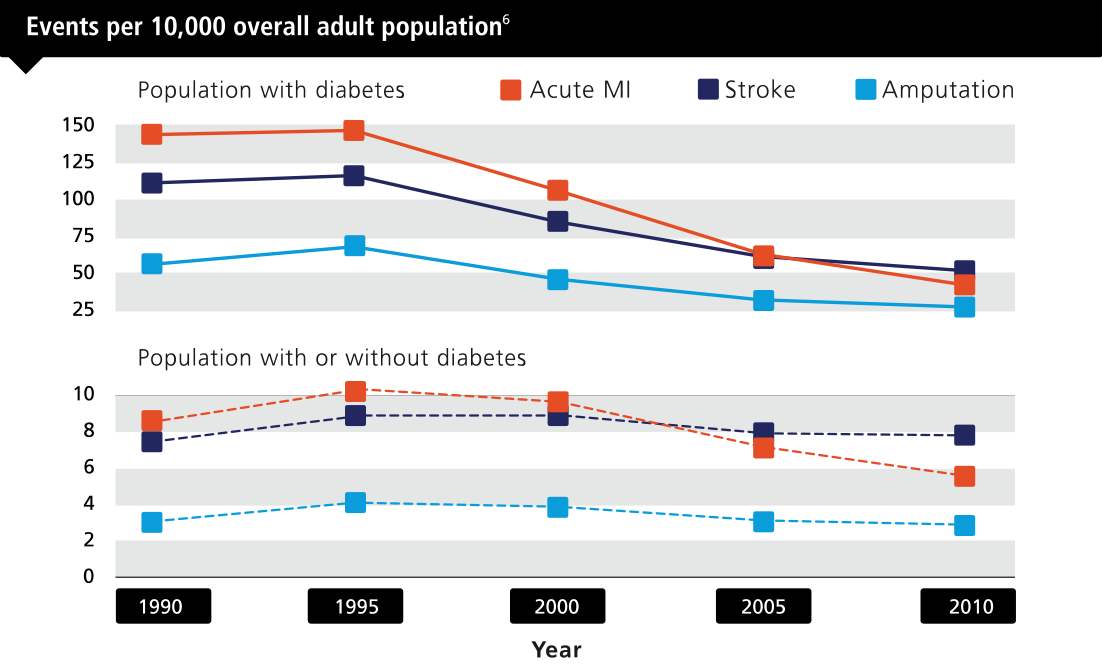
Gregg EW, Li Y, Wang J, et al. Changes in diabetes-related complications in the United States, 1990-2010. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(16):1514-1523.